Last week a solar storm and an asteroid measuring about 3 meters hit our planet, but none of the events posed any risk to people. Meanwhile, new discoveries about the universe were announced.
If you haven’t followed Space News the past few days, enjoy this “summary” and stay on top of all this news!
Scientists are becoming increasingly aware of solar storms, as the Sun will enter its current cycle of peak activity in the coming years. On March 14 and 15, some of them, classified as mild and moderate, arrived on our planet.
Want to be on top of the day’s best tech news? Access and subscribe to our new YouTube channel, Canaltech News. A summary of the headlines from the tech world for you every day!
Such solar storms can cause only minor effects on Earth, such as an increase in the incidence of auroras at certain latitudes on the planet and brief problems with high-frequency radio signals. Solar maximum is expected around July 2025.
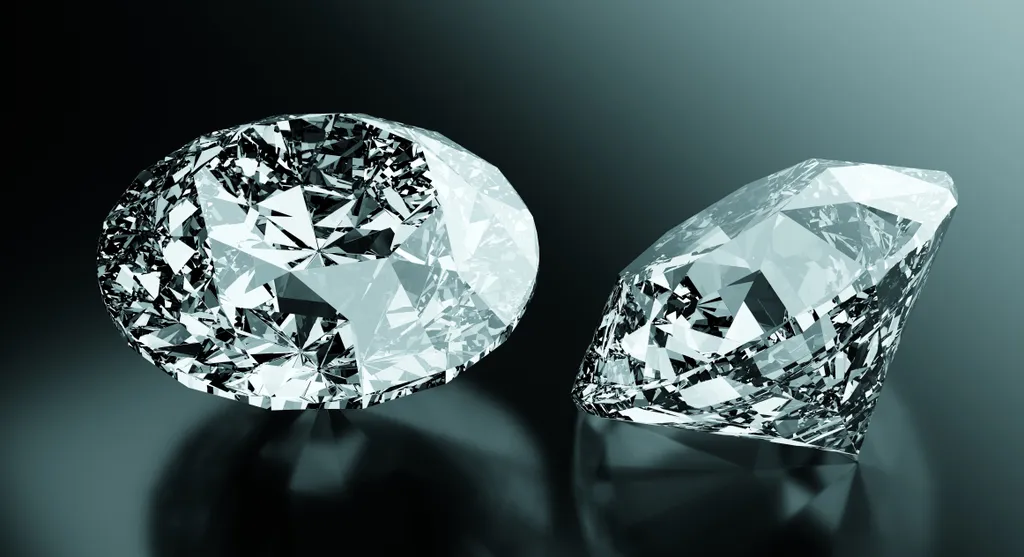

It appears that the impact of falling comets and asteroids at very high speeds on Mercury has turned the carbon that covers most of the planet’s surface into diamonds. The innermost planet in the Solar System may have a layer of graphite more than 90 meters thick, according to a new study.
By the pressure of asteroid impacts, about 60% of graphite can be turned into “shock diamonds”. This would represent about 16 quadrillion tonnes of diamonds out there. But that’s not likely to lead miners to the ultimate adventure in space: Diamonds on Mercury are likely to be impure, along with a messy mix with graphite and other carbon phases.

While there are no potentially dangerous asteroids on a collision course with Earth, none can assure you that there are no other undiscovered space rocks ready to crash into our planet before a telescope can detect them. More or less this happened on Friday (11).
A small asteroid was discovered last Friday (11) by astronomer Kristian Cernezki and just two hours after that, the object crossed Earth’s atmosphere. Fortunately, it was about 3 meters in diameter and would have disintegrated as it passed through the atmosphere. Some Icelanders reported seeing a glow in the sky during the event.

The James Webb Telescope has completed the refinement phase of its instruments, that is, all optical parameters have been verified and tested, and they are working as expected (perhaps even beyond). At the end of the process, James Webb Starr 2MASS J17554042+6551277 . registered to And also the object in the background.
As we can see in the image above, the onboard optical system and camera’s sensitivity make it possible to capture background stars and galaxies. There are still alignments to be done before scientific work with the telescope can begin. in between, James Webb photographed by Gaia Observatory,
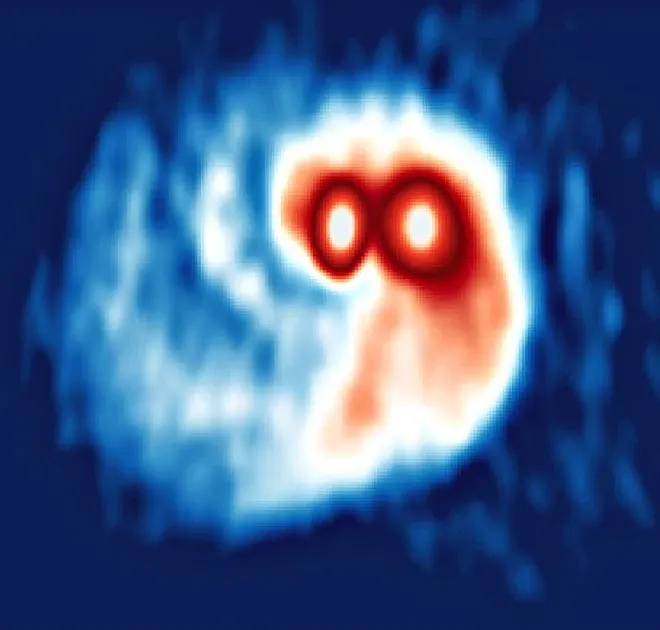
Two stars in the SVS 13 system, located 980 light-years away, were seen with disks of gas and dust around them. These discs appear to be large enough to form new planets and have been identified in unprecedented detail. He discovered about 30 different molecules and 13 complex organic molecules that were the precursors of life.
This is evidence that planet-forming discs may actually exist around stars in binary systems. But it is not clear how, exactly, new planets can form, mainly because the gravitational interaction between the two stars is complex. In addition, a large disc is forming around both stars.
#mars helicopter can not be stopped! Ingenuity successfully completed its 21st flight to the Red Planet. The small rotorcraft traveled 370 meters at a speed of 3.85 meters per second and remained aloft for 129.2 seconds. https://t.co/TNCdXWcKWE pic.twitter.com/rNMaodihxa
— NASA JPL (@NASAJPL) 11 March 2022
hey Ingenuity Helicopter made its 21st flight, traveling 370 meters at a speed of 3.85 m/s. In total, it has already covered a distance of more than 4.6 km since its first flight over the Red Planet. On its final “ride”, the aircraft remained in the air for 129.2 seconds.
With the success of his adventures on Mars, Ingenuity’s mission will be extended until September, The helicopter is expected to assist the Perseverance rover over the next few months as it further tests its flight capabilities in the thin Martian atmosphere.
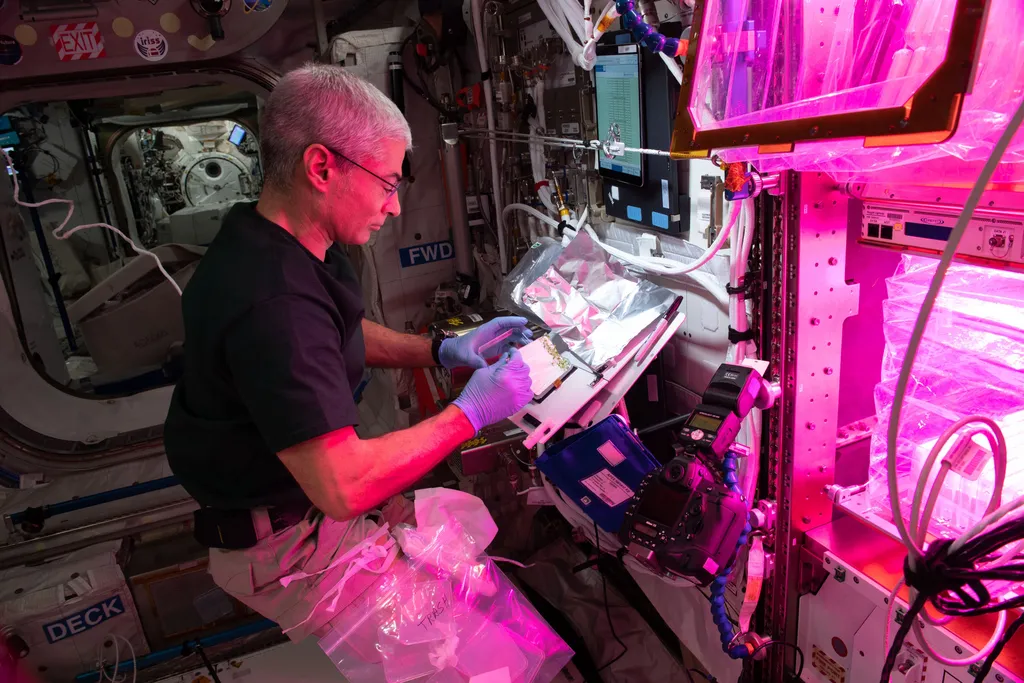

Astronaut NASA Mark Vande Hey broke the record for the longest US spaceflight on Thursday (15). It reached the space station (ISS) in April last year and crossed the 340-day mark on board. Its mission was expected to last six months, but the astronaut’s stay was extended, giving NASA an opportunity to assess the effects of microgravity on long space flights.
The universe’s dark matter, which is probably composed of some kind of hitherto unknown particle, may have multiplied through collisions with particles of “ordinary” matter at the beginning of the universe. This process may explain why dark matter became so much more abundant than what we see in the universe.
According to a new study, shortly after the Big Bang the universe would be compact enough for a series of interactions between particles to occur. Thus, a particle of dark matter and a particle of ordinary matter can collide and produce two particles of dark matter. This would have led to the exponential multiplication of dark matter until the expansion of the universe pushed it away, thus stopping the process of collision.
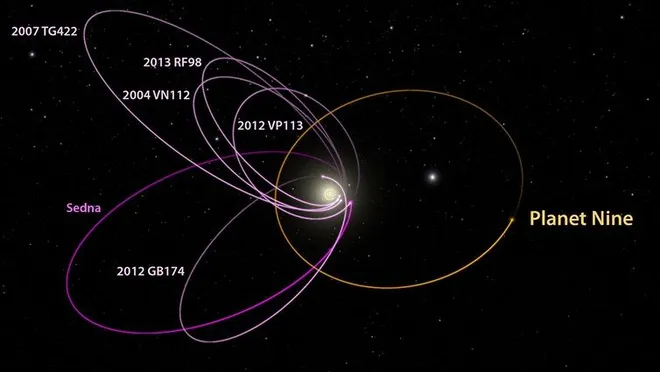
The controversial and hypothetical Planet 9 was not found in a re-scan of the farthest region of the Solar System. Astronomers scanned about 87% of the sky with the Atacama Cosmology Telescope (ACT) to look for the object, which could exist beyond the orbit of Neptune. This led them to rule out the existence of Planet 9 in the studied area with 95% certainty.
If it did exist, the planet would be between 5 and 10 Earth masses, and would orbit the Sun at a distance of 800 astronomical units. But the new results are disappointing, in as much as the presence of this body can explain the strange orbits of other objects already found there.



