Geneva (AFP) – Astrophysicists on Monday printed the greatest-at any time 3D map of the Universe, the result of an investigation of more than 4 million galaxies and extremely-brilliant, power-packed quasars.
The attempts of hundreds of experts from close to 30 institutions around the world have yielded a “comprehensive story of the enlargement of the universe”, explained Will Percival of the University of Waterloo in Ontario, Canada.
In the project released far more than two a long time ago, the researchers produced “the most precise growth record measurements in excess of the widest-ever vary of cosmic time”, he mentioned in a assertion.
The map depends on the latest observations of the Sloan Electronic Sky Study (SDSS), titled the “extended Baryon Oscillation Spectroscopic Survey” (eBOSS), with information gathered from an optical telescope in New Mexico more than 6 decades.
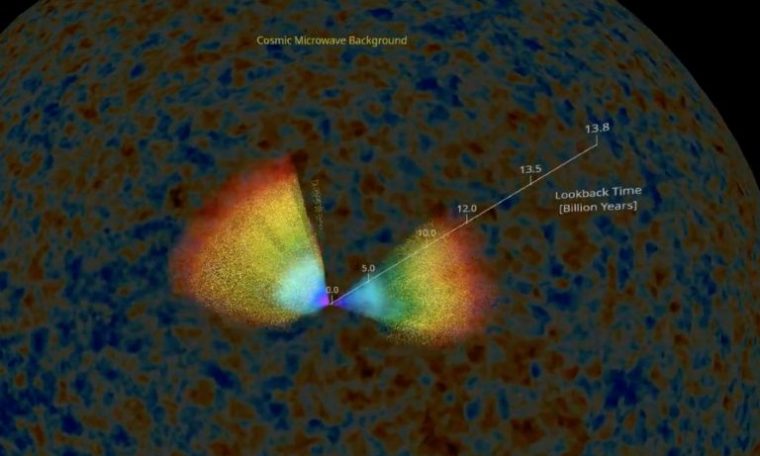
The toddler Universe following the Significant Bang is rather effectively regarded by considerable theoretical products and observation of cosmic microwave background — the electromagnetic radiation of the nascent cosmos.
Scientific studies of galaxies and distance measurements also contributed to a better knowledge of the Universe’s expansion about billions of a long time.
– ‘Troublesome gap’ –
But Kyle Dawson of the University of Utah, who unveiled the map on Monday, explained the researchers tackled a “troublesome gap in the center 11 billion decades”.
As a result of “5 many years of steady observations, we have worked to fill in that hole, and we are utilizing that information and facts to provide some of the most considerable innovations in cosmology in the very last decade,” he said.
Astrophysicist Jean-Paul Kneib of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technologies (EPFL) in Lausanne, who initiated eBOSS in 2012, reported the objective was to create “the most full 3D map of the Universe all over the life time of the Universe”.
For the very first time, the researchers drew on “celestial objects that show the distribution of make any difference in the distant Universe, galaxies that actively sort stars and quasars”.
The map demonstrates filaments of make a difference and voids that much more specifically determine the framework of the Universe since its beginnings, when it was only 380,000 years outdated.
For the aspect of the map relating to the Universe six billion yrs in the past, scientists noticed the oldest and reddest galaxies.
For a lot more distant eras, they concentrated on the youngest galaxies — the blue ones. To go back even further, they applied quasars, galaxies whose supermassive black hole is extremely luminous.
The map reveals that the growth of the Universe started to speed up at some position and has considering that ongoing to do so.
The scientists reported this seems to be because of to the existence of dark strength, an invisible element that suits into Albert Einstein’s normal idea of relativity but whose origin is not yet understood.
Astrophysicists have recognised for many years that the Universe is growing, but have been not able to evaluate the amount of enlargement with precision.
Comparisons of the eBOSS observations with previous reports of the early universe have uncovered discrepancies in estimates of the charge of enlargement.
The presently acknowledged charge, named the “Hubble continual”, is 10 percent slower than the price calculated from the distances amongst the galaxies closest to us.



