Amazing 3D maps of the universe have revealed a single of the most significant cosmic buildings at any time discovered — an almost-inconceivable wall stretching 1.4 billion light-a long time across that consists of hundreds of thousands of galaxies.
The South Pole Wall, as it is really been dubbed, has been hiding in basic sight, remaining undetected right up until now because huge parts of it sit 50 percent a billion light-yrs away guiding the dazzling Milky Way galaxy. The South Pole Wall rivals in sizing the Sloan Wonderful Wall, the sixth largest cosmic structure
Astronomers have long recognized that galaxies are not scattered randomly all through the universe but instead clump alongside one another in what is acknowledged as the cosmic internet hydrogen
Connected: Cosmic history holders: The most significant objects in the universe
Mapping these intergalactic threads belongs to the subject of cosmography, which is “the cartography of the cosmos,” examine researcher Daniel Pomarede, a cosmographer at Paris-Saclay University in France, instructed Reside Science.
Preceding cosmographic do the job has charted the extent of other galactic assemblies, this kind of as the latest structural document holder, the Hercules-Corona Borealis Great Wall, which spans 10 billion mild-many years, or additional than a tenth the sizing of the noticeable universe.
In 2014, Pomarede and his colleagues unveiled the Laniakea supercluster, a galactic selection in which our very own Milky Way
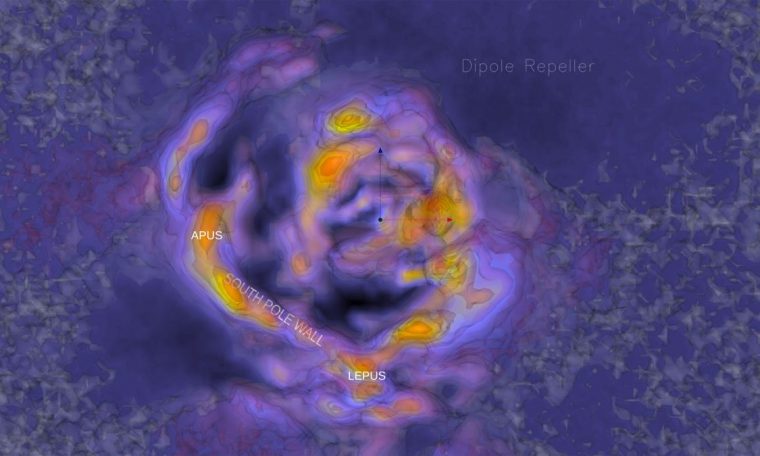
For their new map, the staff used freshly-produced sky surveys to peer into a location identified as the Zone of Galactic Obscuration. This is an space in the southern section of the sky in which the brilliant light of the Milky Way blocks out significantly of what’s powering and close to it.
Cosmographers typically establish the distance to objects working with redshift, the velocity at which an object is receding from Earth astronomer Edwin Hubble
But he and his colleagues utilised a a bit distinctive system, seeking at the peculiar velocity of galaxies. This measurement incorporates redshift but also can take into account the motion of galaxies close to a single another as they tug at every single other gravitationally, Pomarede mentioned.
The edge of the technique is that it can detect hidden mass that is gravitationally influencing how galaxies transfer and as a result uncover dark issue, that invisible things that emits no gentle but exerts a gravitational tug on nearly anything in close proximity to more than enough. (Darkish matter also can make up the bulk of the matter in the universe.) By managing algorithms looking at peculiar movement in galactic catalogs, the group was able to plot the three-dimensional distribution of matter in and all-around the Zone of Galactic Obscuration. Their findings are specific right now (July 9) in The Astrophysical Journal
An all-sky map zoomed in on the South Pole, displaying dust only. In this see, the South Pole Wall is not obvious, though it is near the Chamaeleon sophisticated, a big star-forming area. The bright line ringing the bottom displays the Zone of Galactic Obscuration. (Impression credit: D. Pomarede, R. B. Tully, R. Graziani, H. Courtois, Y. Hoffman, J. Lezmy.)
The resulting map displays a intellect-boggling bubble of materials extra or considerably less centered on the southernmost level of the sky, with a terrific sweeping wing extending north on 1 facet in the way of the constellation Cetus and another stubbier arm opposite it in the path of the constellation Apus.
Relevant: The 12 strangest objects in the universe
Being aware of how the universe looks on these kinds of large scales can help verify our existing cosmological models, Neta Bahcall, an astrophysicist at Princeton College in New Jersey who was not associated in the perform, advised Stay Science. But analyzing where by accurately these massive, crisscrossing buildings commence and finish is tricky, she included.
“When you glance at the community of filaments and voids, it becomes a semantic query of what’s linked,” she stated.
In their paper, the crew acknowledges that they could not have plotted but the entirety of the broad South Pole Wall. “We will not be specific of its entire extent, nor irrespective of whether it is uncommon, right up until we map the universe on a considerably grander scale,” they wrote.
Initially published on Stay Science.